SQL Queries For Practice With Solution
In this article, we will practice basic SQL queries. We will use the HR database while writing queries.
1- Create a Database HR on Default Location
The below query will create the database on default location which was set during the SQL Server installation.
USE master GO CREATE DATABASE HR GO
2- Create a database HR other than default location
This query will save the database on location which is provided in the query. I am going to save database on D drive in DATABASE folder.
USE master GO CREATE DATABASE HR ON PRIMARY (NAME = N'HR', FILENAME = N'D:\DATABASE\HR.mdf' , SIZE = 4096KB , MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED, FILEGROWTH = 1024KB) LOG ON ( NAME = N'HR_log', FILENAME = N'D:\DATABASE\HR_log.ldf' , SIZE = 1024KB , MAXSIZE = 2048GB , FILEGROWTH = 10%) GO
3- Modify database name
This query will rename the name of database HR to HRDB.
USE master GO ALTER DATABASE HR MODIFY NAME = HRDB GO
4- Modify database name using system stored procedure
This query will rename the name of database HRDB to HR using system stored procedure sp_renamedb.
USE master GO EXECUTE sp_renamedb 'HRDB','HR' GO
5- Drop database
The following query will drop the database HR.
USE master GO DROP DATABASE HR GO
To read more about how to create, alter and drop database, Click Here
6- Create table in HR database
The following query will create the table in HR database.
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20), EmpLastName VARCHAR(20), EmpGender VARCHAR(10), EmpAge INT, EmpSalary INT ) GO
7- Modify table name in HR database
The following query will modify the table name from tblEmployee to EmployeeTable in HR database using system stored procedure sp_rename.
The below query will change the table name, but the result will be displayed with the following caution:
Caution: Changing any part of an object name could break scripts and stored procedures.
USE HR GO EXECUTE sp_rename 'tblEmployee', 'EmployeeTable' GO
8- Drop TABLE from database
The following query will delete the table from database.
USE HR GO DROP TABLE EmployeeTable GO
To read about how to create, alter and drop table, Click Here
9- Add PRIMARY KEY on create table
We can add primary key on a column at the time of creating table. This will generate primary key with some random characters at the end of primary key name like below.
PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBA79873D53B4
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20), EmpLastName VARCHAR(20), EmpGender VARCHAR(10), EmpAge INT, EmpSalary INT ) GO
10- Add PRIMARY KEY on ALTER TABLE
We can add primary key on a column after the table is created using ALTER TABLE command. This command will add primary key with a random characters at the end of primary key name like below.
PK__tblEmplo__AF2DBA79EDF0A0BE
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD PRIMARY KEY(EmpID) GO
11- Add Primary Key with Custom Primary Key name
We can add primary key on a column after the table is created using ALTER TABLE command. We can also provide primary key name as below.
PK_tblEmployee_EmpID
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD CONSTRAINT PK_tblEmployee_EmpID PRIMARY KEY(EmpID) GO
12- Add IDENTITY on a column on create table
We can add identity attribute to a column on create table as shown below. IDENTITY can insert the values for column automatically.
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20), EmpLastName VARCHAR(20), EmpGender VARCHAR(10), EmpAge INT, EmpSalary INT ) GO
13- Add FOREIGN KEY on create table
To add a FOREIGN KEY on tblEmployee table, first we create a table tblDepartment with DeptID primary key column and then reference it as a foreign key column in tblEmployee table.
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblDepartment ( DeptID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, DeptName VARCHAR(50) ) GO
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20), EmpLastName VARCHAR(20), EmpGender VARCHAR(10), EmpDeptID INT FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES tblDepartment(DeptID), EmpAge INT, EmpSalary INT ) GO
14- Add FOREIGN KEY on ALTER TABLE
To add a FOREIGN KEY on existing table tblEmployee, use the following query.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD FOREIGN KEY(EmpDeptID) REFERENCES tblDepartment(DeptID) GO
15- Add FOREIGN KEY on ALTER TABLE with custom name
When we create foreign key at the time of create table or on alter table without writing the name for foreign key then SQL Server will generate the foreign key name by adding the some random character at the end.
To give foreign key a sensible name we can mention the foreign key name as.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD CONSTRAINT FK_tblEmployee_tblDepartment FOREIGN KEY (EmpDeptID) REFERENCES tblDepartment(DeptID); GO
16- Add UNIQUE KEY on create table
In the below create table statement we create a table tblEmployee with a EmpUserName with a UNIQUE KEY constraint.
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20), EmpLastName VARCHAR(20), EmpUserName VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE, EmpGender VARCHAR(10), EmpDeptID INT, EmpAge INT, EmpSalary INT ) GO
17- Add UNIQUE KEY on alter table
In the below query we add the UNIQUE KEY constraint on existing table.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD UNIQUE(EmpUserName) GO
18- Add UNIQUE KEY on alter table with custom name
In the below query we add the UNIQUE KEY constraint with custom name on existing table.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD CONSTRAINT UQ_tblEmployee_EmpUserName UNIQUE(EmpUserName) GO
19- Drop UNIQUE KEY from table
In the below query we can delete the UNIQUE KEY constraint from a table.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee DROP CONSTRAINT UQ_tblEmployee_EmpUserName GO
20- Add DEFAULT constraint on create table
The below query will show you how to add default constraint on EmpJoiningDate column when creating a table.
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20), EmpLastName VARCHAR(20), EmpGender VARCHAR(10), EmpAge INT, EmpSalary INT, EmpJoiningDate DATETIME DEFAULT GETDATE() ) GO
21- Add DEFAULT constraint on alter table
The below query will show you how to add default constraint on already created table with alter table command.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD DEFAULT GETDATE() FOR EmpJoiningDate GO
22- Add DEFAULT constraint on alter table with custom default name
The below query will show you how to add default constraint with custom default constraint name on already created table with alter table command.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD CONSTRAINT DF_tblEmployee_joiningDate DEFAULT GETDATE() FOR EmpJoiningDate GO
23- CHECK constraint on create table
The below query will show you how to add CHECK constraint while creating a table. We will add CHECK constraint on EmpAge column to limit the age greater than or equal to 18 years.
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20), EmpLastName VARCHAR(20), EmpGender VARCHAR(10), EmpAge INT CHECK(EmpAge>=18), EmpSalary INT, EmpJoiningDate DATETIME ) GO
24- CHECK constraint on alter table
The below query will show you how to add CHECK constraint by altering the table. We will add CHECK constraint on EmpAge column to limit the age greater than or equal to 18 years.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD CHECK(EmpAge>=18) GO
25- CHECK constraint on alter table with custom name
The below query will show you how to add CHECK constraint by altering the table with custom name. We will add CHECK constraint on EmpAge column to limit the age greater than or equal to 18 years with custom name as.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ADD CONSTRAINT CHK_tblEmployee_EmpAge CHECK(EmpAge>=18) GO
26- Drop CHECK constraint
The below query will drop the CHECK constraint.
USE HR GO ALTER TABLE tblEmployee DROP CONSTRAINT CHK_tblEmployee_EmpAge GO
27- Create table and Insert records in tables
So far, we have seen how to apply keys and constraints on tables one by one.
Now, First we will create tblDepartment, tblGender and tblEmployee tables with proper keys and constraint and then do some practical examples.
Table tblEmployee has EmpID column as primary key and identity, EmpUserName has Unique key constraint, EmpGender and EmpDeptID columns are reffered as Foreign key constraint, EmpAge has Check constraint and EmpJoiningData column has Default constraint.
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblDepartment ( DeptID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, DeptName VARCHAR(50) ) GO
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblGender ( GenderID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL, Gender VARCHAR(50) ) GO
USE HR GO CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, EmpLastName VARCHAR(20) NULL, EmpUserName VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE NOT NULL, EmpGenderID INT FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES tblGender(GenderID), EmpDeptID INT FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES tblDepartment(DeptID), EmpAge INT CONSTRAINT CHK_tblEmployee_EmpAge CHECK(EmpAge>=18), EmpSalary INT NULL, EmpJoiningDate DATETIME CONSTRAINT DF_tblEmployee_EmpJoiningDate DEFAULT GETDATE() ) GO
28- Insert Multiple Rows using multiple INSERT INTO statements
Let’s insert rows in tblDepartment table. We can use multiple INSERT INTO statements to insert values in a table.
USE HR GO INSERT INTO tblDepartment VALUES(1,'HR') INSERT INTO tblDepartment VALUES(2,'Research and Development') INSERT INTO tblDepartment VALUES(3,'Purchase') INSERT INTO tblDepartment VALUES(4,'Sale')
29- Insert Multiple Rows using single INSERT INTO statements
Let’s insert rows in tblGender table. We can use single INSERT INTO statements to insert values in mutiple rows of a table.
USE HR GO INSERT INTO tblGender VALUES (1,'Male'), (2,'Female') GO
Let’s insert rows in tblEmployee table.
USE HR GO INSERT INTO tblEmployee (EmpFirstName, EmpLastName, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpDeptID, EmpAge, EmpSalary, EmpJoiningDate) VALUES ('Davio','Nancy','Davio Nancy',1,1,25,50000,'2010-01-01'), ('Fuller','Andrew','Fuller Andrew',1,1,20,40000,'2010-06-01'), ('Leverling','Janet','Leverling Janet',1,2,35,50000,'2010-07-01'), ('King','Robert','King Robert',1,3,22,25000,'2010-01-01'), ('Ali','Hassan','Ali Hassan',1,1,30,75000,'2010-08-01'), ('Zahid','Ali','Zahid Ali',1,2,25,50000,'2011-01-01'), ('Sara','Ali','Sara Ali',2,3,25,50000,'2011-09-01'), ('Suman','Shah','Suman Shah',2,1,20,30000,'2011-12-01'), ('Anne','Andrew','Anne Andrew',2,3,33,35000,'2012-01-01'), ('Ammara','Khan','Ammara Khan',2,2,25,50000,'2013-01-01') GO
30- SELECT ALL rows from tblDepartment table(using *)
In below query we will get all rows using * (asterisk).
USE HR GO SELECT * FROM tblDepartment GO
Result

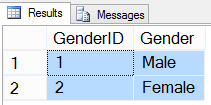
31- SELECT ALL rows from tblGender table(using Column names)
In below query we will get all rows by writing all column names.
USE HR GO SELECT GenderID, Gender FROM tblGender GO
Result
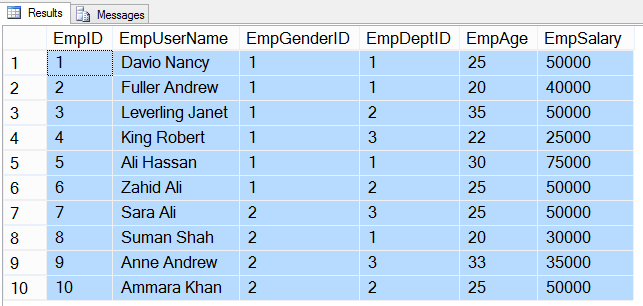
32- SELECT rows with specific columns from tblEmployee table
In below query we will get all rows with specific columns
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpDeptID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee GO
Result
33- SELECT filtered rows using WHERE clause
In below query we will get filtered rows with specific columns whose EmpDeptID is 1.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpDeptID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpDeptID = 1 GO
Result

34- SELECT filtered rows with multiple conditions using AND operator
In below query we will get filtered rows with specific columns whose EmpDeptID is 1 AND EmpGenderID is 2.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpDeptID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpDeptID = 1 AND EmpGenderID = 2 GO
Result

35- SELECT filtered rows with multiple conditions using OR operator
In below query we will get all filtered rows with specific columns whose EmpDeptID is 1 OR EmpGenderID is 2. The result will be all rows whose EmpDeptID is 1 either whose EmpGenderID is 2.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpDeptID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpDeptID = 1 OR EmpGenderID = 2 GO
Result

36- SELECT filtered rows with NOT(! or <>) operator
In below query we will get all filtered rows with specific columns whose EmpGenderID is not 1.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpDeptID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpGenderID != 1 GO
Result

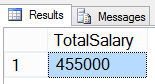
37- SELECT sum of salary from tblEmployee table
In below query we will get sum of salaries from tblEmployee table using SUM() aggregate function.
USE HR GO SELECT SUM(EmpSalary) AS TotalSalary FROM tblEmployee GO
Result
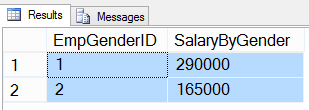
38- SELECT sum of salary by gender from tblEmployee table
In below query we will get sum of salaries with EmpGenderID.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpGenderID, SUM(EmpSalary) AS SalaryByGender FROM tblEmployee GROUP BY EmpGenderID GO
Result
39- SELECT average salary from tblEmployee table
In below query we will get average salary from tblEmployee table using AVG() function.
USE HR GO SELECT AVG(EmpSalary) AS AvgSalary FROM tblEmployee GO
Result

40- SELECT average salary by gender from tblEmployee table
In below query we will get average of salaries with EmpGenderID.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpGenderID, AVG(EmpSalary) AS AVGSalaryByGender FROM tblEmployee GROUP BY EmpGenderID GO
Result

41- SELECT total number of employees from tblEmployee table
In below query we will get number of all rows using COUNT() aggregate function.
USE HR GO SELECT COUNT(*) AS TotalEmployees FROM tblEmployee GO
Result

42- SELECT minimum salary from tblEmployees table
In below query we will get the minimum salary from tblEmployee table using MIN() aggregate function.
USE HR GO SELECT MIN(EmpSalary) AS MinSalary FROM tblEmployee GO
Result

43- SELECT maximum salary from tblEmployees table
In below query we will get the maximum salary from tblEmployee table using MAX() aggregate function.
USE HR GO SELECT MAX(EmpSalary) AS MaxSalary FROM tblEmployee GO
Result

44- SELECT rows where EmpUserName starting with letter 'a'
In below query we will get all the rows whose EmpUserName starts with the letter ‘a’ using wildcard ‘%’.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpUserName LIKE 'a%' GO
Result

45- SELECT rows where EmpUserName ends with letter 'n'
In below query we will get all the rows whose EmpUserName ends with the letter ‘n’ using wildcard ‘%’.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpUserName LIKE '%n' GO
Result

46- SELECT rows where EmpUserName having 'k' anywhere in the EmpUserName
In below query we will get all the rows whose EmpUserName having character ‘k’ anywhere in the EmpUserName.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpAge, EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpUserName LIKE '%k%' GO
Result

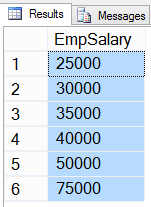
47- SELECT DISTINCT rows using DISTINCT keyword
In below query we will get unique salary from tblEmployee table using DISTINCT keyword.
USE HR GO SELECT DISTINCT EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee GO
Result
48- SQL Arithmetic Operators
Below is the SELECT query with all arithmetic operators as follows.
USE HR GO SELECT (10+5) AS Addition, (10-5) AS Subtraction, (10*5) AS Multiplication, (10/5) AS Division, (10%5) AS Modulus GO
Result

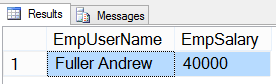
49- SQL Comparison Operators, Equal(=)
Below is the query to get all rows from tblEmployee table where EmpSalary is equal to 40000.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpUserName,EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpSalary=40000 GO
Result
50- SQL Comparison Operators, Greater than(>)
Below is the query to get all rows from tblEmployee table where EmpSalary is greater than 40000.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpUserName,EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpSalary>40000 GO
Result

51-SQL Comparison Operators, Less than(<)
Below is the query to get all rows from tblEmployee table where EmpSalary is less than 40000.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpUserName,EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpSalary<40000 GO
Result

52-SQL Comparison Operators, Greater Than or Equal(>=)
Below is the query to get all rows from tblEmployee table where EmpSalary is greater than or equal to 40000.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpUserName,EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpSalary>=40000 GO
Result

53-SQL Comparison Operators, Less Than or Equal(<=)
Below is the query to get all rows from tblEmployee table where EmpSalary is less than or equal to 40000.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpUserName,EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpSalary<=40000 GO
Result

54-SQL Comparison Operators, Not Equal to (!= or <>)
Below is the query to get all rows from tblEmployee table where EmpSalary is not equal to 40000. We can use two symbols != or <> for not equal to operator.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpUserName,EmpSalary FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpSalary!=40000 GO
Result

55-Backup table using SELECT INTO statement with all rows and columns
Using the below query we will backup the tblEmployee table with all rows and columns. tblEmployee_Backup_1 is the name of the backup table which will be created and data inserted into it.
USE HR GO SELECT * INTO tblEmployee_Backup_1 FROM tblEmployee GO
Result

56-Backup table using SELECT INTO statement with selected columns
Using the below query we will backup the tblEmployee table with all rows and the selected number of columns. tblEmployee_Backup_2 is the name of the backup table which will be created and data inserted into it.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpAge, EmpSalary, EmpJoiningDate INTO tblEmployee_Backup_2 FROM tblEmployee GO
Result

57-Backup table using SELECT INTO statement with selected columns and filtered rows
Using the below query we will backup the tblEmployee table with selected rows and the selected number of columns. tblEmployee_Backup_3 is the name of the backup table which will be created and data inserted into it.
USE HR GO SELECT EmpID, EmpUserName, EmpGenderID, EmpAge, EmpSalary, EmpJoiningDate INTO tblEmployee_Backup_3 FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpGenderID=1 GO
Result

58-Update a row in tblEmployee table
In the below query, we will update the EmpAge of an employee whose EmpID is 1.
USE HR GO UPDATE tblEmployee SET EmpAge=30 WHERE EmpID=1 GO
Result

59-Update multiple rows in tblEmployee table
In the below query, we will update the EmpSalary of an employee whose EmpAge is greater than or equal to 30000.
USE HR GO UPDATE tblEmployee SET EmpSalary=60000 WHERE EmpAge>=30 GO
Result

60-Delete a row from tblEmployee table
In the below query, we will delete a row from tblEmployee table whose EmpID is 10.
USE HR GO DELETE FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmpID=10 GO
Result
As we deleted the row whose EmpID is 10. Then there will be no more record with an EmpID 10.

So far, we learned basic SQL queries with practical examples. In the next article, we will learn Advanced SQL Queries For Practice With Solution.
Recommended Readings
- Advanced SQL Queries For Practice With Solution
- SQL Queries For Practice With Solution
- SQL Interview Questions and Answers
- STORED PROCEDURE in SQL Server
- How To Join Tables Data in SQL Server
- How to use Transaction in SQL Stored Procedure
- Difference Between IN and NOT IN Operators in SQL
- How To Modify Date in SQL Using DATEADD
- How To Get Year From Date in SQL Server
- How To Get Month From Date in SQL Server
- How To Get Day From Date in SQL Server
- How To Use ROW_NUMBER Function in SQL
- Date and Time Functions in SQL Server
- How To Find Nth Highest Salary in SQL Server
- How to Backup Table Using SELECT INTO Statement
- How To Use HAVING Clause in SQL Server
- Aggregate Functions in SQL Server
- How To Group Data Using Group By in SQL Server
- How To Truncate Table in SQL Server
- How To Delete Data From Table in SQL Server
- How To Update Table Data in SQL Server
- How To Sort Data Using Order By Clause in SQL
- How To Select Distinct Records in SQL Server
- How to Filter Data From Table in SQL Server
- Round Off Values Using Ceiling and Floor in SQL
- How To Find Square Root Of A Number in SQL Server
- How To Select Data From Table in SQL Server
- How To Insert Data in SQL Server Table
- How To Add NOT NULL Constraint in SQL Server
- How To Add Check Constraint on SQL Server Table
- How To Add Default Constraint on SQL Server Table
- Unique Key Constraint in SQL Server
- How to add Foreign Key Constraint in SQL Server
- How To Add Identity To SQL Server Table Column
- How to add Primary Key Constraint in SQL Server
- How To Create Alter and Drop Table in SQL Server
- How To Create Alter and Drop Database in SQL